As a guardian of your family's health, you understand the importance of clean drinking water. You've likely considered a home water purifier to ensure the water pouring from your taps is free of contaminants. But navigating the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) standards for these devices isn't always straightforward.
You need to sift through various guidelines, certifications, and testing reports to find the right fit for your home. It's not just about picking any filter off the shelf; it's about understanding what those numbers and acronyms mean for the safety of your water. Will the system you choose adequately remove the specific impurities found in your local water supply?
As you consider the maze of regulations and certifications, remember that the right knowledge can lead to peace of mind—and the wrong assumption could leave unseen risks flowing from your faucets.
Let's explore how you can confidently select a water purifier that meets EPA standards and suits your needs, all while ensuring you stay compliant with an ever-evolving landscape of environmental regulations.
Understanding EPA Water Standards
To ensure your tap water's safety, it's critical to comprehend the EPA's Safe Drinking Water Act, which mandates stringent contaminant levels that public water systems must adhere to. The SDWA establishes maximum contaminant levels (MCLs), serving as a Drinking Water Filtration Fact that underpins environmental protection and public health.
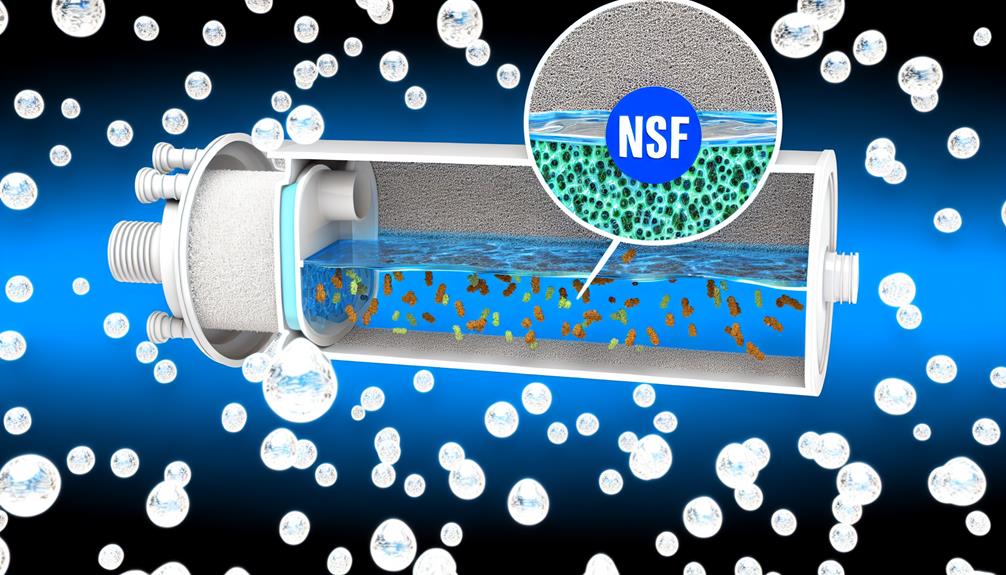
When considering home water filtration, it's essential to recognize that not all treatment systems are equal. Filtration technologies, such as reverse osmosis, must satisfy EPA regulatory requirements. By opting for certified systems that align with NSF Standards, you ensure the removal efficiency meets stringent industry criteria.
Stay informed about both federal and state regulations. Some states might impose additional standards, further safeguarding Water and Drinking Water quality. The NSF International certification is a hallmark of performance verification. Selecting a product bearing this certification means you're choosing a treatment system proven to reduce specific contaminants effectively.
Moreover, regularly review your Consumer Confidence Reports (CCRs). These reports provide a snapshot of your drinking water's quality. If the CCR indicates potential concerns, a tailored home water filtration system may be necessary to meet or exceed the recommended guidelines, thereby ensuring the safety and purity of your tap water.
Certification Processes Explained
Understanding the certification process for home water purification systems is crucial, as it confirms that the equipment adheres to established standards for effectively removing contaminants. When you're sifting through Drinking Water Information and considering Home Drinking Water Filtration options, you'll want to ensure your choice is backed by a reliable certification process. Here's what you need to know:
- Certifying Bodies: Organizations like NSF International conduct rigorous testing to certify filtration systems. They verify that systems meet specific standards, such as NSF/ANSI 42 for aesthetic effects and NSF/ANSI 53 for health effects, ensuring your water filtration unit performs as advertised.
- Industry Standards: Certified systems comply with industry standards for contaminant reduction. This means you can trust that the certified equipment will deliver clean, safe drinking water, aligning with the expectations set by Series Filtration Facts and the Drinking Water Treatment guidelines.
- Homeowner Benefits: While you aren't held to the same regulatory requirements as public water systems, using certified filtration systems offers peace of mind by aligning your home's water purity with EPA standards.
Certification processes are designed to answer your Frequently Asked Questions about water quality and safety. By choosing a certified filtration system, you're not just buying a product; you're investing in verified water safety for your home.
Common Contaminants and Limits
Grasping the spectrum of common contaminants regulated by the EPA, including lead, chlorine, and pesticides, is essential as you select a home water purifier designed to tackle these specific impurities within the established maximum contaminant levels (MCLs). When considering the health of your home drinking water, it's vital to understand that the EPA's MCLs serve as a baseline for safety, not a definitive ceiling for contaminant presence.
Delving deeper into the Series Filtration Facts, you'll find that each contaminant's MCL is carefully determined based on potential health risks. For example, lead, a neurotoxin, has an action level at 15 parts per billion. Exceeding this limit can be detrimental to health, particularly in children. Chlorine, while used for disinfection, must remain below 4 parts per million to avoid harmful effects.
As you explore information on home water purifiers, consider that some filtration systems are specifically tailored to reduce certain contaminants more effectively. Moreover, you shouldn't overlook state-specific regulations that may impose stricter standards beyond the EPA's guidelines.
To address frequently asked questions regarding home drinking water, always ensure that the filtration system you choose is certified against the common contaminants and limits set by both federal and state EPA standards. This due diligence guarantees a safeguarded water supply aligned with the highest purification benchmarks.
Compliance Tips for Manufacturers
Manufacturers must meticulously ensure their water filtration systems meet or exceed EPA regulatory requirements for contaminant removal to remain compliant. As you navigate the complexities of these standards, consider the following:
- Seek certification from reputable programs such as NSF International to validate your system's efficacy against contaminants.
- Conduct regular testing to verify your system maintains performance in line with industry benchmarks.
- Stay informed about federal and state regulations to ensure full compliance across different markets.
Your filtration products should come with detailed instructions for homeowners, addressing questions regarding home drinking water safety. This advice on home water system maintenance is a critical component of the Health Series Filtration Facts you provide.
Moreover, the document contains information about the Series Filtration Facts, which can serve as a valuable resource for both consumers and manufacturers. In your Frequently Asked Questions section, be sure to include comprehensive Compliance Tips for Manufacturers. This proactive approach not only positions you as an expert but also encourages trust and transparency with your customers.
Lastly, encourage users to provide feedback on their experience with your products. This input can help refine your offerings and ensure that they continue to meet the stringent standards set by the EPA.
Monitoring and Reporting Requirements
To ensure your home water purifier remains effective and compliant, it's essential to adhere to the EPA's monitoring and reporting requirements. These requirements include regular contaminant testing and meticulous record-keeping. As part of a series of standards aimed at safeguarding home drinking water, these requirements serve as a critical checkpoint in the filtration process.
Your technical expertise comes into play when selecting methods to monitor the specific contaminants outlined by the EPA. You'll need to conduct these tests periodically, aligning with the frequency recommended by the standards. It's not just about running tests; you also have to analyze the facts, interpreting the data to ensure your filtration system consistently meets performance benchmarks.
Reporting entails a disciplined approach. You must maintain detailed records of all test results and submit this data to the designated authorities when necessary. This reporting demonstrates your purifier's compliance and effectiveness in real-time scenarios.